Demo
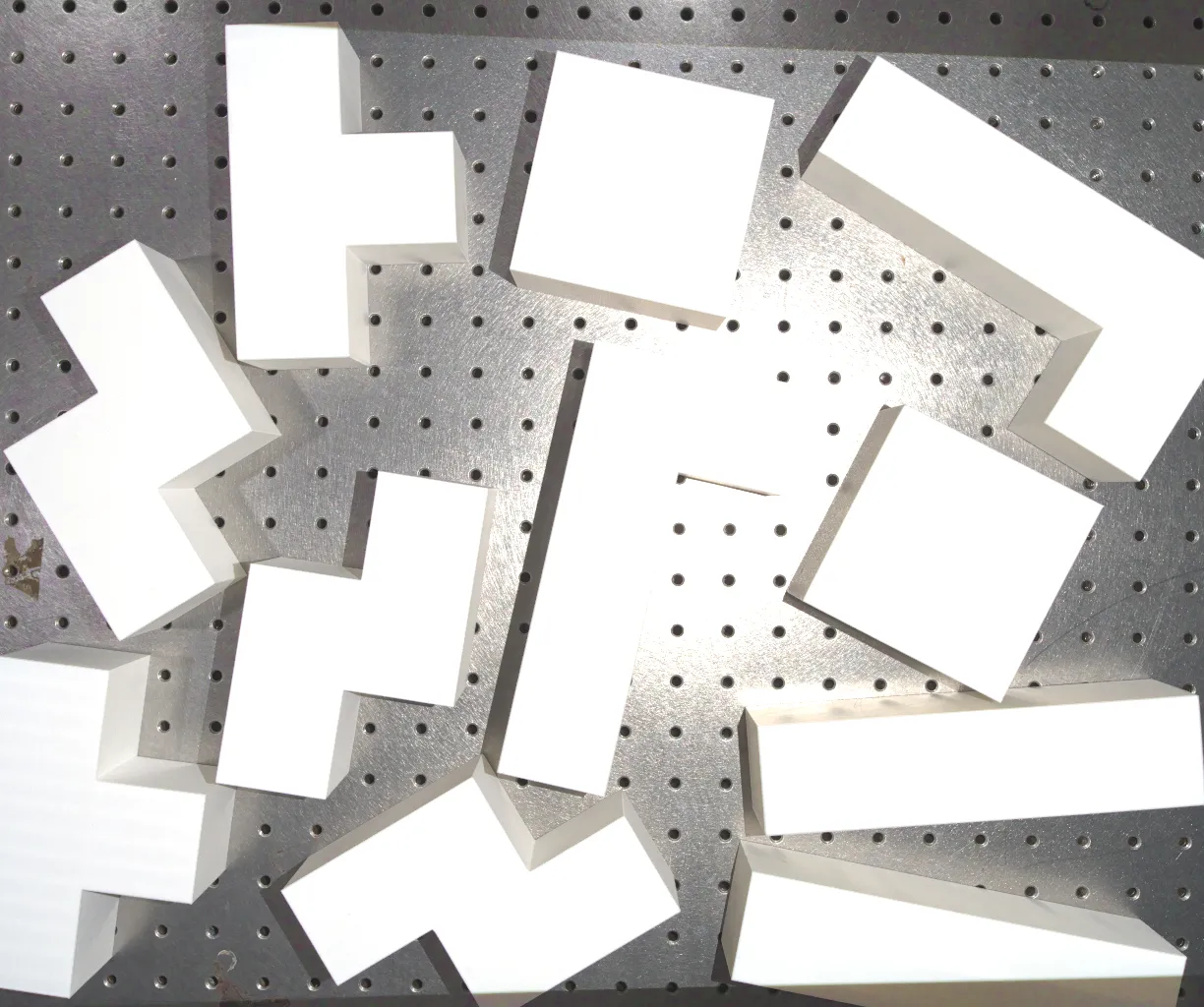

3D point cloud captured from Zivid camera
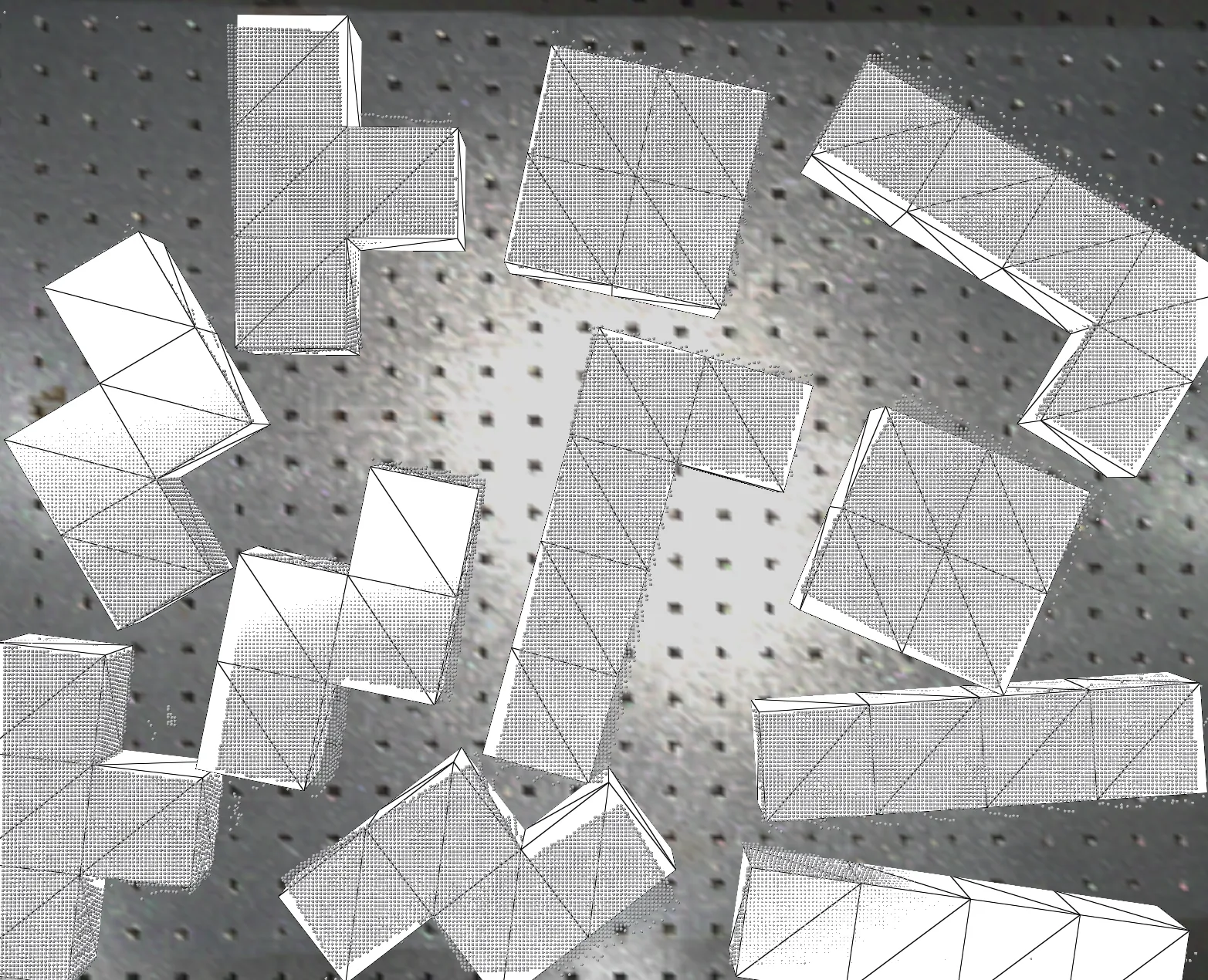
Network predictions with 6D pose bounding boxes
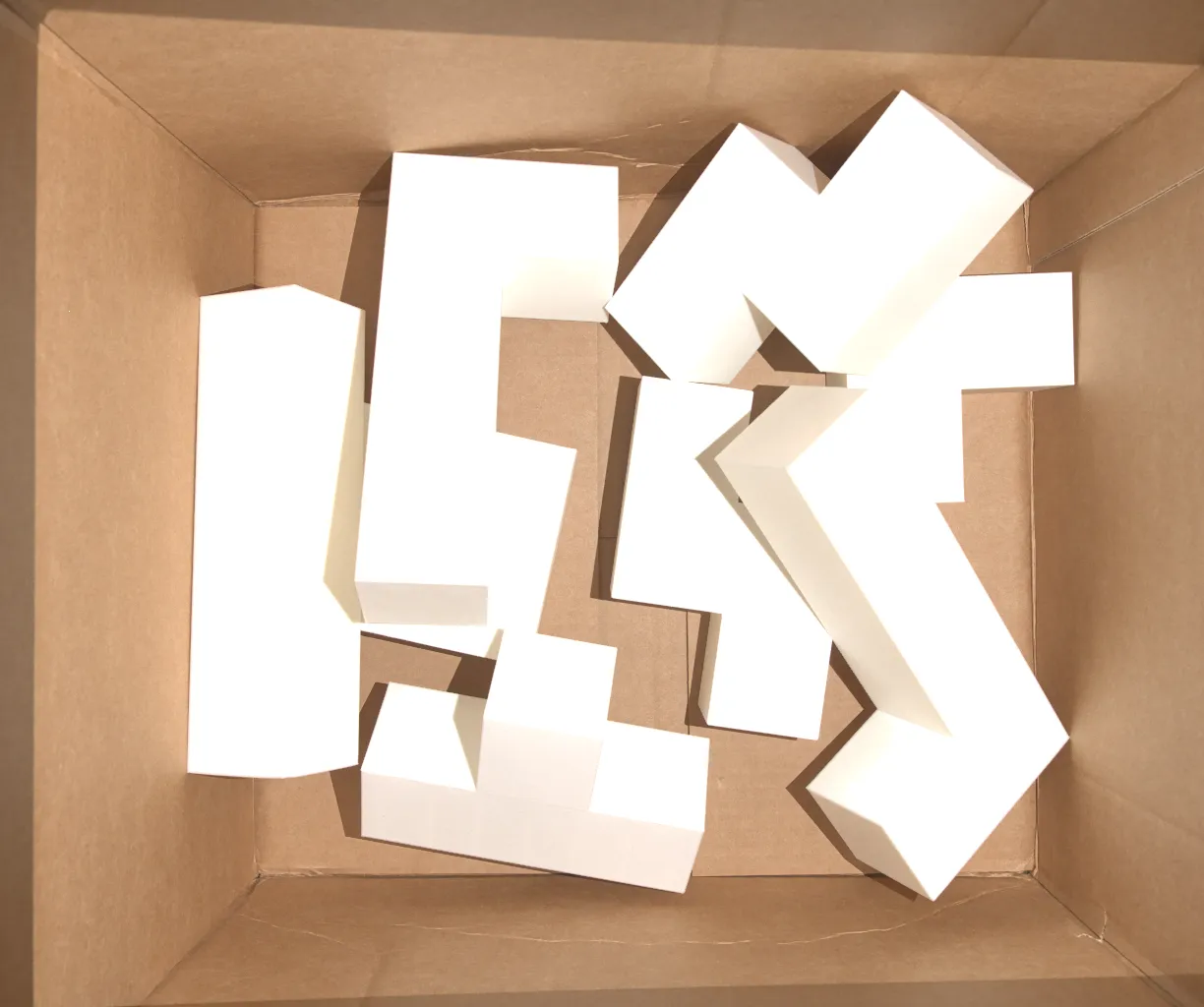

Tetris in cluttered bin
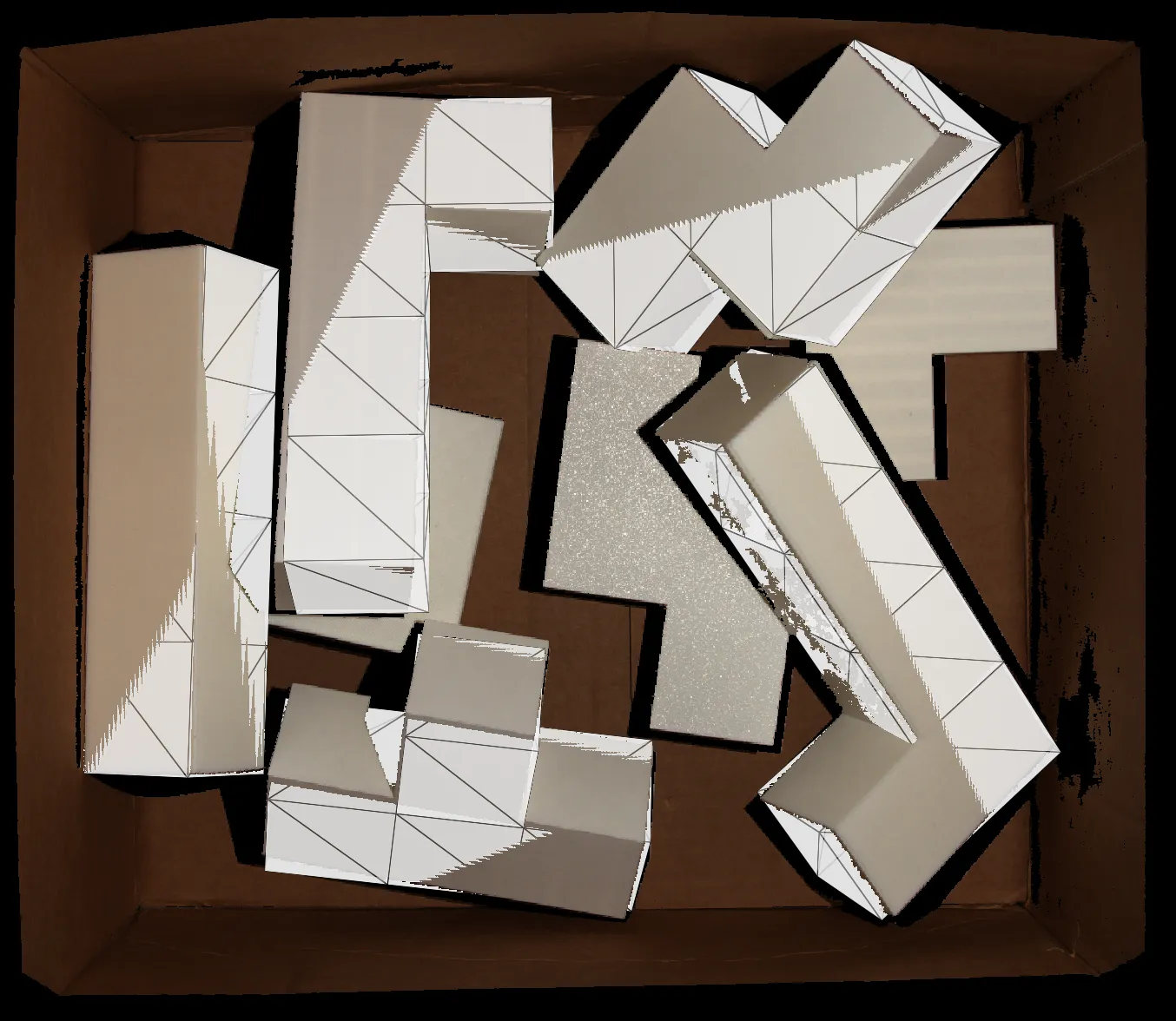

6D pose prediction in cluttered bin
Background
Robotic bin picking requires solving multiple hard problems simultaneously:
- 3D perception in clutter - objects heavily occluded and randomly oriented
- RGB methods fail - lighting variations, textureless surfaces, depth ambiguity
- Instance segmentation at scale - traditional pipelines need separate detection + segmentation + pose networks
- Sim-to-real gap - models trained on synthetic data often fail in real deployment
I built Tetris-PoseNet combining 3D deep learning and robotic integration to deliver: point cloud direct processing + end-to-end pose prediction + robust sim-to-real transfer.
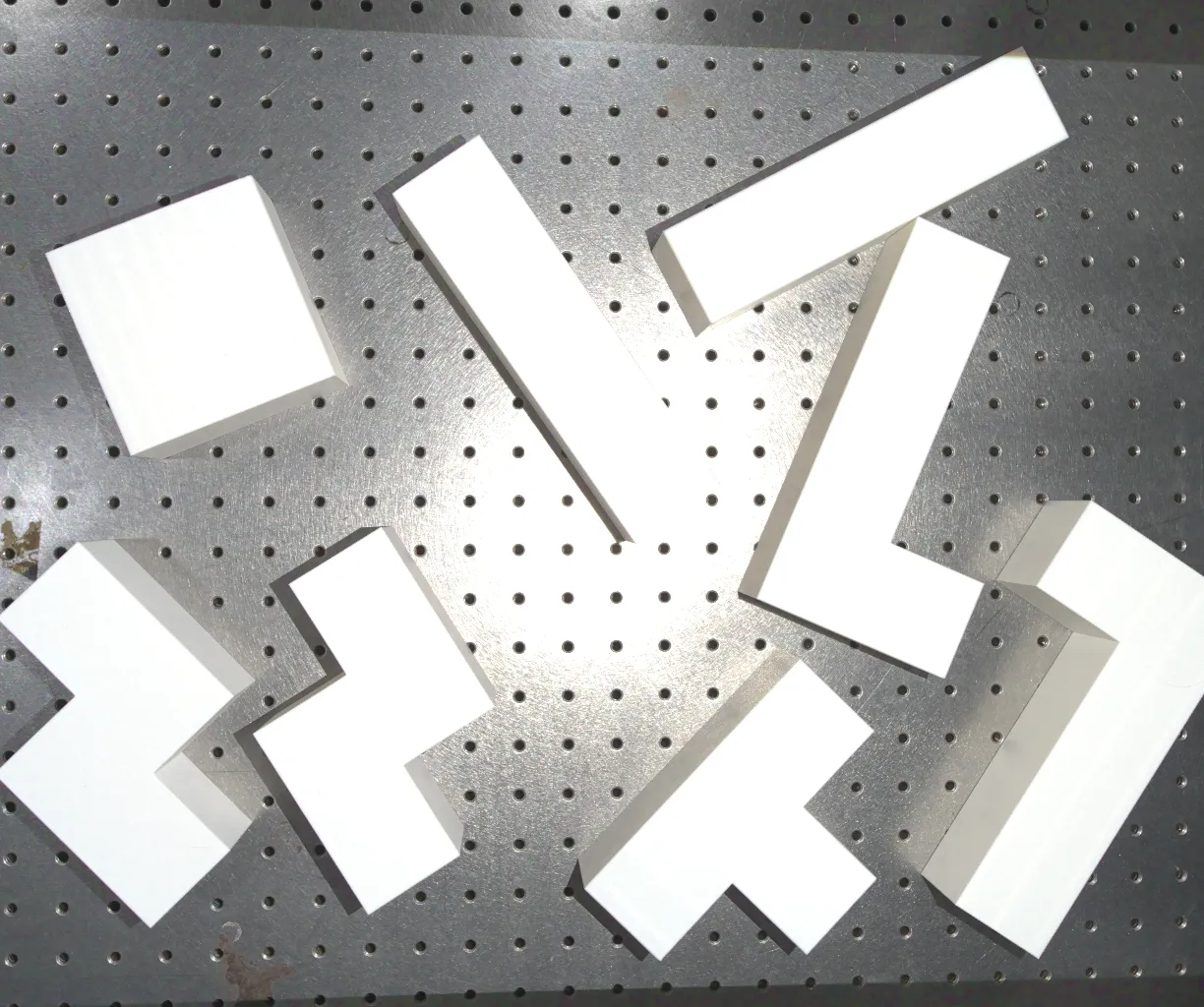

Table calibration using plane fitting
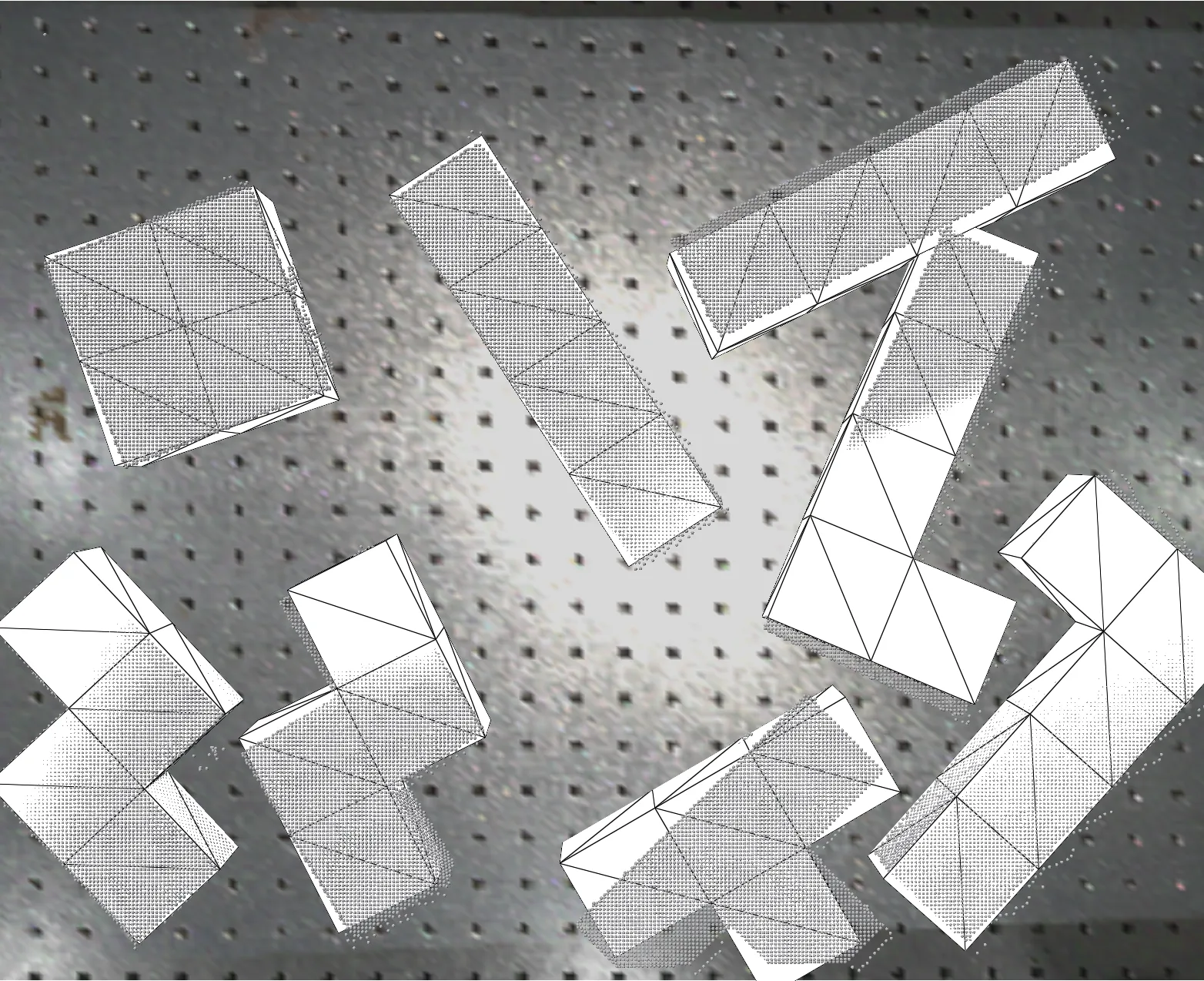
Validated predictions in calibrated frame

Hand-eye calibration using 3D scan

Successful grasp execution
References
Research Foundation:
- Point Transformer V3 - State-of-art point cloud backbone
- PPR-Net - Point-wise pose regression framework
Technical Stack:
- PyTorch Lightning - Distributed training framework (6-GPU DDP)
- Point Transformer V3 - Self-attention point cloud backbone
- MuJoCo & pyBullet - Physics simulation for synthetic data
- Hydra - Config-driven architecture (swappable backbones)
Things I Learned
Deep Learning at Scale:
- Distributed training orchestration (6x RTX 5880 scaling)
- Curriculum learning from single-object to dense clutter
- Symmetry-aware loss functions for rotational invariance
3D Vision:
- Point cloud transformers vs. voxel methods
- Sim-to-real gap challenges (sensor noise, material properties)
- Camera-robot calibration precision requirements
System Integration:
- Real-time pipeline optimization (<200ms perception-to-action)
- Modular design with Hydra configs (PointNet++/DGCNN/PTV3 swapping)
- Production deployment debugging (network inference + robot control)
Acknowledgments
Supervisor: Prof. Ziqi Wang, HKUST
Lab Resources: Von Neumann Institute, HKUST
